6 - Supply, Demand, and Government Policies#
6.1 - The Surprising Effects of Price Controls#
A price ceiling is a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold.
A price floor is a legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold.
How Price Ceilings Affect Market Outcomes#
If the price that balances supply and demand is below a price ceiling, that price ceiling is not binding.
If the equilibrium price is above the price ceiling, the ceiling has a binding constraint on the market. This creates a shortage of the good.
When the government imposes a binding price ceiling on a competitive market, a shortage arises, and sellers must ration scarce goods among potential buyers.
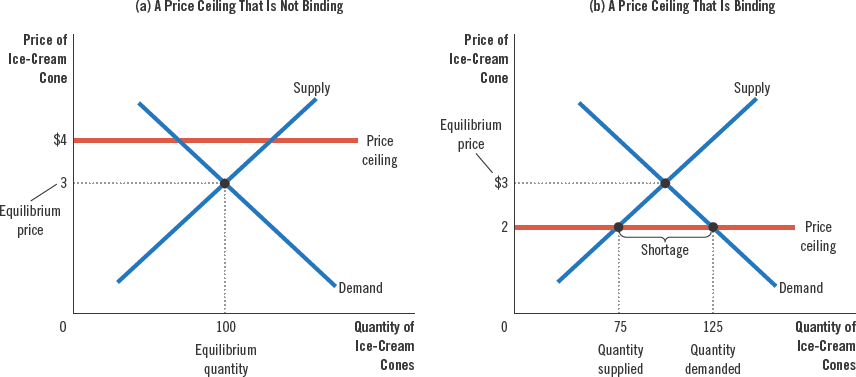
Rent control is a common example of price ceilings. In the long run, when the supply and demand curves are more elastic, this leads to major housing shortages (note that this effect is present but less pronounced in shorter terms).
How Price Floors Affect Market Outcomes#
If the equilibrium price is below the price floor, it is is binding. A binding price floor causes a surplus.
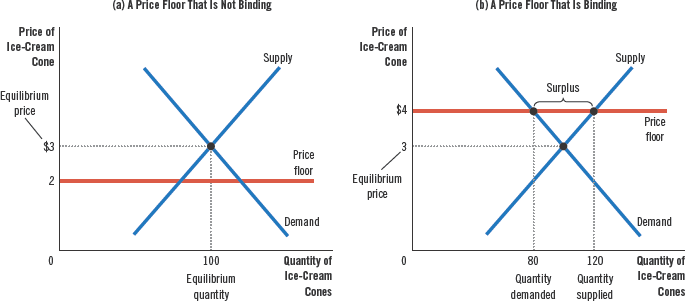
The main example of price floors is minimum wage. A binding price floor on labor creates a labor surplus, which means high unemployment.
Evaluating Price Controls#
Helping those in need can be done in ways other than raising the minimum wage (e.g. earned income tax credit, rent and wage subsidies). The policies tend to work better, but they are not perfect, since applying for programs can place a burden on those in need and maintaining these programs requires tax dollars.
6.2 - The Surprising Study of Tax Incidence#
Tax incidence is the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a market.
How Taxes on Sellers Affect Market Outcomes#
A tax on sellers shifts the supply curve but does not affect the demand curve. This shift of the supply curve is to the left, since the quantity supplied is lowered. As a result, the equilibrium price rises and the equilibrium quantity lowers.
Because the price rises and the quantity lowers, the tax burden is shared among buyers and sellers.
How Taxes on Buyers Affect Market Outcomes#
A tax on buyers shifts the demand curve but does not affect the supply curve. This shift of the demand curve is to the left, since the quantity demanded is lowered. As a result, the equilibrium price rises and the equilibrium quantity lowers.
Because the price rises and the quantity lowers, the tax burden is shared among buyers and sellers.
Because the effects of taxing buyers and sellers are the same, we call raising the taxes on buyers and/or sellers a tax wedge.
Elasticity and Tax Incidence#
The tax burden is not typically shared equally between buyers and sellers.
A tax burden falls more heavily on the side of the market which is less elastic. This is because the more elastic side of the market is more willing and able to leave the market.
