24 - Smalltalk#
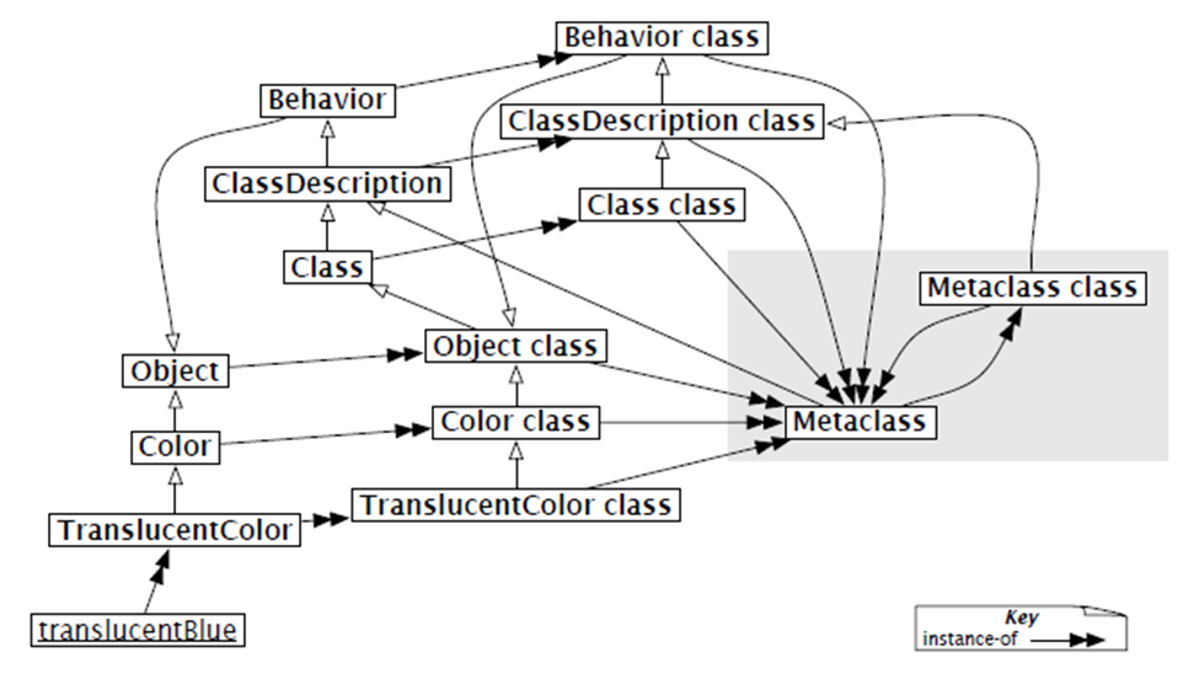
There are 5 main classes in the Smalltalk class hierarchy:
Object
Behavior
ClassDescription
Metaclass
Class
Object#
Object is the root of the Smalltalk class system. All classes in the system are its subclasses.
Printing#
printString, displayStringprintOn: aStringdisplayOn: aStreamdisplay, displayNlprint, printNl
Testing Membership#
classisMemberOf:isKindOf:respondsTo:superclass
Comparison#
=~===~~isNilisArray
Copying (Shallow and Deep)#
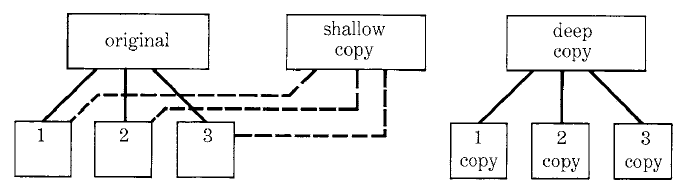
x:=Set new. x add: 1; add: 2.
y:='second'. z:='third'.
a:=Array new: 3.
a at:1 put:x. a at:2 put:y. a at:3 put:z.
b:=a.
c:=a copy.
d:=a deepCopy.
a printNl. b printNl. c printNl. d printNl.
a at: 2 put: '2nd'.
(a at: 1) add: 3.
a printNl. b printNl. c printNl. d printNl.
Metaclass#
Whenever a new class is created, a new metaclass is created for it automatically.
A metaclass only has one instance.
A metaclass does not have a class name. A metaclass can be accessed by sending its instance the unary message
class.The messages categorized as “class methods” in the class descriptions are found in the metaclass of the class.
All metaclasses are the instances of a class called
Metaclass.
Behavior#
Parent class of all “class” type classes.
Default
newornew:method defined here.It describes the subclass/superclass relationships between classes, contains information about instance variables, and holds the method dictionary that’s associated with each class.
ClassDescription#
ClassDescription represents class naming, class commenting, and naming instance variables.
It is reflected in additional protocol for accessing the name and the comment, for adding and removing instance variables.
It also organizes methods by the category.
Metaclass#
Metaclass provides methods for the creation of actual class objects from the metaclass object and the creation of metaclass objects.
Class#
Just like Object is a class that models all instances, Class is a class that models all classs.
It contains information commonly attributed to classes: namely, the class name, class comment, class variables, class pool dictionary, and the class category.
